Home | | Syllabus | | Assignments | | Lecture Notes
Topics for Exam 1:
This sheet is intended to help you prepare for the first midterm in this course. The exam will cover
through section 4.3 in the textbook and lecture #12 on February 12. The following lists topics
covered in the first 5 weeks of the course that may appear on the exam.
1. Abstract Data Types
2. Classes in C++
3. Stacks and Queues
4. Pointers
5. Linked Lists
The following problems are intended to help you study for the exam, however topics not covered here may be on the exam as well. Use your text, class notes, labs and assignments to review for the exam as well.
1) Write a function that counts how many even numbers there are in an integer linked list. The function should have one parameter, a pointer to a linked list. The function should not alter the list. It should return an integer value equal to the number of even numbers in the list.
You can assume the following definitions:
struct Node {
int data;
Node *next;
Node();
Node(Node_entry item, Node *add_on = NULL);
}
2) Consider the following code:
int *y; int *x; x = new int; *x = 15; *x += 2; y = x; *y *= 2;
a) Draw a diagram to represent the pointers as each line of this code is executed.
b) What are the values of *x and *y after executing this code?
3) What is the output of the following Code?
typedef int Stack_entry;
typedef int Queue_entry;
int main(void) {
Stack pile;
Queue lineUp;
int number;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++ )
pile.push(i * 2);
lineUp.append(i + 2);
}
while (!pile.empty()) {
pile.top(number);
pile.pop( );
cout << number << " ";
}
cout << endl;
while (!lineUp.empty()) {
lineUp.retrieve(number);
lineUp.serve();
cout << number << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
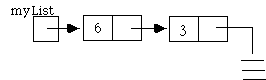
4) Consider the following linked list:

Assume a Node is represented by the following struct:
struct Node {
int myNumber;
Node *nextNode;
Node();
Node(Node_entry item, Node *add_on = NULL);
};
a) Write an expression to refer to the integer in the second node of the list.
b) What is the value of the following expression?
c) Write the C++ code to create and insert a new node, whose data value is 4, in between the two nodes of myList.
5. Consider the following class declarations:
class Student {
public:
void SetUp( char name[ ], int idNum);
void Write( ) const;
void SetGpa(float gpa);
Student ( );
Student (char initName[ ], int initId);
private:
char name [25];
int id;
float gpa;
};
class StudentYear : public Student {
public:
void SetUp( char name[ ], int idNum, int year);
void Write ( ) const;
void incrementYear( );
StudentYear ( );
StudentYear (char initName[ ], int initId, int initYear);
private:
int year;
};
a) Which class is the parent class and which is the child class?
b) Which function is the same for both the Student and the StudentYear class?
c) Which private data members can be accessed directly by the member functions of each class?
d) What specific kind of function is StudentYear( )?
6. Write a function to replace the serve() function of the Queue class with the function, Error_code ServeTwo( ), to delete the first two items in the queue and return an appropriate error code. Assume the Queue representation we developed in class, using a circular array implementation. Recall the Queue specification:
const int maxqueue =10 ; //small value for testing
class Queue {
public:
Queue();
bool empty()const;
Error_code serve();
Error_code retrieve(Queue_entry &item) const;
Error_code append(const Queue_entry &item);
private:
int count, front, rear;
Queue_entry entry [maxqueue ];
};
7) In addition to being able to solve the above problems, you should be able to describe, in your own words, the concepts learned in the course. For example, what is a destructor function and why is it needed? What is the importance of data hiding? Etc.