CSCI 150, Spring 2003
Home | | Course Schedule | | Assignments | | Lecture Notes
Practice Problems
The following problems are intended to help you study for the exam.
1)Given these boolean variables:
x = true, y = false, z = true
What is the value (true/false) of each of the following?
i) x and (y or z)
Answer: true
ii) (not x) or (not(y and z))
Answer: true
iii) y or (x and not z)
Answer: false
2)Write a program that does the following:
Prompt the user to input a number.
Input the number from the keyboard
If the number is less than 100, write:
XX is a low number.
where XX refers to the number inputted by the user.
Otherwise, write:
XX is a high number.
program lowOrHigh;
var
number : integer;
begin
writeln('Enter a number:');
readln(number);
if number < 100 then
begin
writeln(number, ' is a low number.');
end
else
begin
writeln(number, ' is a high number.');
end;
end.
3) Compute the value of the following expressions:
a) 6 / 3 * 2
Answer: 4
b) (17 - 11) / 3 + 3
Answer: 5
c) Add parentheses to part b so that the addition is performed
before the division.
Answer: (17 - 11) / (3 + 3)
d) What is the value of c) ?
Answer: 1
4) a) What is the value of sum after the execution of the following code?
sum := 0; for counter := 1 to 4 do begin sum := sum + 2 * counter; end; Answer: 20
5) What is the output of the following code fragment (mySentence and partial are both strings)?
mySentence := 'It was a dark and stormy night'; partial := copy(mySentence, 8, 6); writeln(partial); Answer: a dark6) What is wrong with the following fragments of Pascal?
program p1;
var
p2: integer
begin
p2 := 1;
end.
Answer: The semi-colon after the word integer is missing (on line 3).
program s1;
var
s2: string;
begin
s2 := '1';
end.
Answer: The indentation is inconsistent and confusing.
program r1;
begin
if true then
writeln('Truth is beauty.');
end;
end.
Answer: The word begin is missing after the 'if true then' line (line 3).
program t1;
var
circumference: real;
radius: real;
begin
circumference := 3.14159265 radius * radius;
end.
Answer: The * is missing between 3.14159265 and radius.
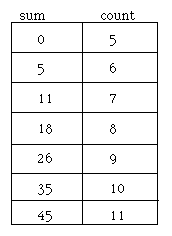
7) Consider the following while loop: sum := 0; count := 5; while count <= 10 do begin sum := sum + count; count := count + 1; end;
a) Fill in the following table for the values of count and sum each time through the loop (there may be more rows than you need in the table):

b)Write a for loop that does the equivalent of the above loop.
sum := 0; for count := 5 to 10 do begin sum := sum + count; end;
8. Consider the following pascal code:
program z3;
var
sum,i: integer;
begin
sum := 0;
for i :=1 to 4 do
begin
sum := sum + i;
end;
writeln(sum);
end.
What is value of sum printed on the screen?
Answer: 10
9. Fill in/write the necessary code for the following decision tree.

program catCheck (input, output);
var
answer : string;
begin
writeln('Do you have a cat?');
readln(answer);
if answer = 'yes' then
begin
writeln('What kind is it?');
readln(answer);
if answer = 'Siamese' then
begin
writeln('Good choice!');
end
else if answer = 'Tiger' then
begin
writeln('Another good choice.');
end
else if answer = 'Calico' then
begin
writeln('I have never had that kind.');
end;
end
else
begin
writeln('You should get one.');
end;
end. {end of main program catCheck}
10. Fill in the necessary code to fill in the depositList array with deposit amounts entered by the user. You should keep track of the sum of all the deposits made, so that the print statement at the end of the program makes sense. You can assume there are exactly 1000 deposits made.
program deposit;
type
realArray : array [1..1000] of real;
var
loop : integer;
sum : real;
depositList : realArray;
begin
sum := 0;
for loop := 1 to 1000 do
begin
writeln('Enter deposit');
readln(depositList[loop]);
sum := sum + depositList[loop];
end;
writeln ('The sum of the deposits: $', sum:5:2);
end;