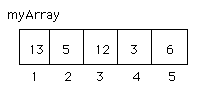
CSCI 150, Spring 2003
Home | | Course Schedule | | Assignments | | Lecture NotesHere is an array of integers:
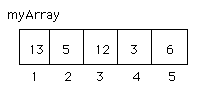
Referring to elements of the array:
The position of an element in an array is given by the index. The name of the array, followed by
the index is used to refer to a particular element:
Declaring and array: Arrays are declared by first creating a type that refers to an array of some length and data type. The array is then declared as a variable of the array type:
type intArray5 = array[1 . . 5] of integer; var myArray: intArray5;
Using elements of an array:
Elements of the array can be used in the same way as variables of the same data type can be used.
I.e. an element of an array of integers can be used anywhere an integer variable can be used.
myArray[4] := 3;
myArray[5] := myArray[4]*2;
writeln('The fifth element of the array is ', myArray[5]);
m := 3;
myArray[m] := 12;
Using arrays with for loops.
Arrays go naturally with for loops as illustrated in the following examples:
1) Assigning values to each element of the array:
type intArray5 = array[1 .. 5] of integer; var evens: intArray5; count: integer; begin for count := 1 to 5 do begin evens[count] := 2 * count; end; end.
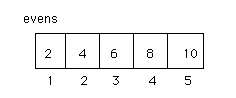
2) Reading in values for each element of an array:
type
realArray12 = array[1 .. 12] of real; {Array of 12 real numbers}
var
bill: realArray12;
count: integer;
begin
for count := 1 to 12 do
begin
writeln('Enter amount of bill ');
readln(bill[count]);
end;
end.
3) Finding the sum of elements in an array:
sum := 0.0;
for count := 1 to 12 do
begin
sum := sum + bill[count] ;
end;
writeln('The total is ', sum);
4) Finding the minimum value of elements in an array:
minimum := bill[1];
for count := 2 to 12 do
begin
if bill[count] < minimum then
begin
minimum := bill[count];
end;
end;
writeln('The minimum is ', minimum);