CSCI 110
Home | | Course Schedule | | Assignments | | Lecture NotesThe following topics have been covered in the final part of the course. Each of the following topics may appear on the exam. In addition there may be questions on any of the topics covered in the earlier parts of the course.
1. Machine Architecture
Computer organization
CPU with registers (IP, IR, CF, AX)
Memory
P88 Assembly language (you do not need to memorize the instructions, but you
should understand how to use the instructions to write a program)
Fetch Execute cycle
Language Translation
2. History of the Internet
Origin of the internet--ARPAnet.
How the internet evolved
Organizations that oversee the internet
3. TCP/IP
Protocols--Purpose, types of protocols (TCP/IP, HTTP)
Packet Switching
Function of TCP and IP in sending and receiving email
How email is transmitted across the network.
4. The World Wide Web
Definition of World Wide Web (difference from Internet)
Purpose of Hypertext
The Client/Server Model
Universal Resource Locators (URLs)
5. Hypertext Markup Language (HTML)
Standard form of an HTML file
Common HTML tags (as listed in course notes)
Adding Images, Links and Graphics to your page
Absolute vs. Relative addressing
Coloring the background of your page
HTML Tables
6. Web Graphics
Monitor resolution and image size
Color representations
Bit Depth
Color Tables
RGB Hexadecimal Color notation
Graphic File compression (GIF and JPEG)
7. Tractable and Intractable problems
Definition of tractable and intractable problems
Examples of Intractable Problems
(e.g. Tower of Hanoi or Traveling Salesman).
8. Noncomputability
Non-computable functions
The halting problem
Other non-computable problems
9. Other limits of computing
Limits to storing integers and real numbers
Hardware limitations (hardware failure, etc.)
Limitations in communication (noise, error checking)
Practice Problems
The following problems are intended to help you study for the exam. In addition, you should
review the problems from the first two review sheets, along with your homework and labs.
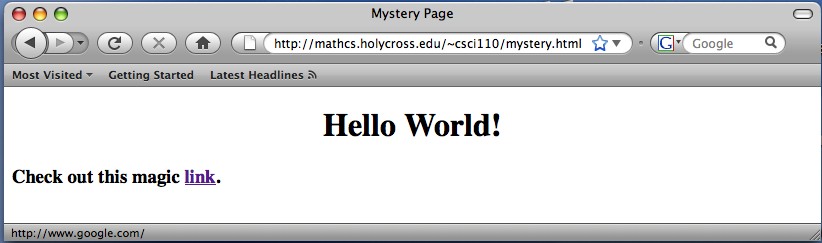
1. Use the web page screen shot given in Figure 1 to answer the following questions. This screen-shot was taken when the mouse was over the link.

Figure 1. Screen shot of web page for problem 1
b. What is the title of the web page?
c. Where does the link go?
d. What is the name of the web server that this page is served from?
e. Write the HTML file that would generate this page. Hint: Headlines of size 1 and 3 are in this page.
2. The following equations give the running times (t) of different algorithms with respect to the size of the input (n). For each, state whether the problem is tractable or intractable:

3. The following table gives the running time of an algorithm for different input sizes:
Size time(secs) 1 0.5 2 2.0 3 4.5 4 8 5 12.5 ... ... 10 50 100 5000
b) Based on the values given, do you think this algorithm is tractable or intractable? Why?
4. Protocols.
b) List three protocols that we covered in class, and briefly state their functions.
5. What color does #FF00FF represent in the RGB color representation?
6. Suppose an image file has a bit depth of 8, a width of 100 pixels and a height of 200 pixels.
b) What is the size of the image if displayed on a monitor with a resolution of 50 ppi (pixels per inch)?
7. Briefly describe what "packet switching" means and how it is used on the internet.
8. What is a non-computable function? Describe 2 problems that are non-computable.
9. Suppose you want to prove that a given problem was non-computable with a proof by contradiction. What are the 2 steps you must accomplish for such a proof?
10. Write an assembly language (P88 instructions) to read in two numbers. If the first is bigger, it should print out the first number. Otherwise the program should print nothing and end.
11. Write a Python program to read words into a list until the word "stop" is entered. Count the number of words entered that start with the letter 'a' and print out that number and the contents of the list.
#program aCounter.py myWords = [ ] #Add entered numbers to this list #add your python code here