CSCI 110
Home | | Course Schedule | | Assignments | | Lecture NotesThe following topics have been covered in the second part of the course. Each of the following topics may appear on the exam. In addition there may be questions on any of the topics from the first part of the course.
1. Functions Divide and conquer programming Writing function definitions Calling a function Execution of a function Formal and actual parameters Returning a value from a function 2. Recursion Definition of recursion Writing a recursive function (one that calls itself) Classic examples of recursion: Fibonacci, Factorial 3. Writing classes Writing a class definition Specifying class properties Specifying class methods (functions) Using self The constructor function (__init__( )) The __str__( ) function Creating an object Calling class functions with an object (dot notation) 4. Church-Markov-Turing Hypothesis 5. Binary representation Counting in base 2 Converting from decimal to base 2 (and back) Hexadecimal representation (base 16) Integer representation Signed magnitude, One's complement, Two's complement Binary arithmetic Floating point representation 6. Digital Circuits Components: Logic switches, AND, OR, NOT, NAND, NOR and XOR Writing Truth tables for circuit outputs Writing logical expressions to describe circuit outputs Designing a circuit to compute a logical expression
Practice Problems
The following problems are intended to help you study for the exam. Solutions
to these problems will be posted on the CSCI 110 website. You should try to solve the
problems before looking at the solutions!
1) Given the function definition: def Mystery( someVal): answer = 0 if someVal > 2.0: answer = 3.0 * someVal else: answer = 0.0 return answerWhat is the value is assigned to x after execution of the following statement?
x = Mystery(2.5)2) Consider the following program:
def Demo( theList, answer): theList[0] = theList[0]*2 answer = theList[0] + 3.5 myList = [20] myResult = 4.8 Demo(myList, myResult) print myList print myResultWhat is printed out?
3) a)Write a function,
def sumOfIntegers( n ):that returns the sum of all integers from one to n.
b) Write a Python statement to compute the sum of integers from 1 to 100 using the above function and store the answer in the variable, hundredSum.
4) What is the output of the following program?
#program: review.py import sys def reverse(word, n): if n < 0: print else: sys.stdout.write(word[n]) reverse(word, n-1) myWord = "back" reverse(myWord, len(myWord) -1)5) a) Write a class, Student, that has three properties, gradYear, name and gpa.
b) Write Python code to creat a Student object, setting the name to "Jane Doe", the graduation year to 2010 and the gpa to 3.75. Invoke the printInfo( ) function for this object to print out the student's information.
6) a) Convert the following numbers to binary representation:
237 45 63b) Convert the above numbers to hexadecimal representation
7) For each of the following numbers, show their representations in each of: signed magnitude, 1's complement and 2's complement:
22 -31 -22 498) Using eight bit numbers, add the following two binary numbers:
01110001 00011100Show your work. Convert the result to decimal.
9) Draw a circuit that computes the following truth table for inputs a and b and output c:
| a | b | c |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
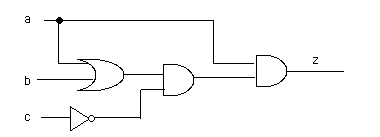
10) Write an expression for the output of the following circuit. Draw a truth table that shows the output for each combination of inputs:
